Учебное пособие по английскому языку для обучающихся 1-2 курсов предназначено для ознакомление с укладом жизни англоговорящих стран. Учебное пособие содержит тексты, упражнения, задания, вопросы по темам.
- Меню
- Главная
- Дошкольное образование
- Начальные классы
- Астрономия
- Биология
- География
- Информатика
- Математика
- Алгебра
- Геометрия
- Химия
- Физика
- Русский язык
- Английский язык
- Немецкий язык
- Французский язык
- История
- Естествознание
- Всемирная история
- Всеобщая история
- История России
- Право
- Окружающий мир
- Обществознание
- Экология
- Искусство
- Литература
- Музыка
- Технология (мальчики)
- Технология (девочки)
- Технология
- Физкультура
- ИЗО
- МХК
- ОБЖ
- Внеурочная работа
- ОРК
- Директору
- Завучу
- Классному руководителю
- Экономика
- Финансовая грамотность
- Психологу
- ОРКиСЭ
- Школьному библиотекарю
- Логопедия
- Коррекционная школа
- Всем учителям
- Прочее
Создайте Ваш сайт учителя Курсы ПК и ППК Видеоуроки Олимпиады Вебинары для учителей
- Главная
- Английский язык
- Уроки
- Учебное пособие по ангийскому языку
Учебное пособие по ангийскому языку
Просмотр содержимого документа
«Учебное пособие по ангийскому языку»
ГОСУДАРСТВЕННОЕ БЮДЖЕТНОЕ ПРОФЕССИОНАЛЬНОЕ ОБРАЗОВАТЕЛЬНОЕ
УЧРЕЖДЕНИЕ РОСТОВСКОЙ ОБЛАСТИ
«ТАГАНРОГСКИЙ МЕХАНИЧЕСКИЙ КОЛЛЕДЖ»
Учебное пособие
по английскому языку
для обучающихся 1-го курса
на тему «Англоговорящие страны»
разработал: преподаватель
английского языка
ГБПОУ РО «ТМехК»
Ороева И.Б.
2016
ENGLISH- SPEAKING COUNTRIES
Read, translate the texts, study the words and expressions and do some exercises.
Text A: “English-speaking countries”





1) The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland is situated on the islands in the northwest of Europe.
The Atlantic ocean is on the north of it and the North Sea to the east. The English Channel (21 miles) separates it from the continent. Great Britain is the largest island/. The three main parts of it are Scotland, England and Wales. Northern Ireland is situated on the island called Ireland.
The population of the United Kingdom is about 60 million and its capital is London.
The United Kingdom is a highly developed country. Its main cities are London, Birmingham, Manchester and Glasgow.
2) The United States of America (USA) is located in North America. It is one of the largest countries in the world. The population of the USA is about 250 million people. The USA has 50 states. Its capital is Washington D.C. (the District of Columbia). Its main cities are New York, Chicago, San Francisco, Los Angeles and Boston.
It is a highly developed country. People of very many nationalities live in the USA.
3) Canada is situated in North America. Three oceans surround it: the Atlantic, the Arctic and the Pacific. The capital of the country is Ottawa. About 30 million people live in Canada.
It is a great industrial country. Its main cities are Ottawa, Toronto, Montreal and Vancouver.
4) Commonwealth of Australia occupies the continent of Australia and a number of islands (the main one of which is Tasmania). It includes 6 states and 2 territories with a population of about 20 million people.
Its capital is Canberra and the main cities are Sidney and Melbourne.
5) New Zealand consists of several large and many smaller islands. Its population is about 4 million people. The capital is Wellington.
The chief cities are Auckland, Dunedin and Nelson.
It is a highly developed agricultural country.
Vocabulary:
agricultural – сельскохозяйственный
Auckland – Окленд
be situated – быть расположенным
Birmingham – Бирмингем
main part – основная часть
Vancouver - Ванкувер
Manchester – Манчестер
Washington - Вашингтон
Montreal – Монреаль Wellington - Веллингтон
nationality – национальность
Boston – Бостон
Nelson - Нельсон
Canberra – Канберра
New York – Нью -Йорк
Channel – канал
occupy – занимать, захватывать
Chicago – Чикаго
Ottawa - Оттава
Chief – главный
preference - предпочтение
Commonwealth – содружество
principal – главный, основной
consist of – состоять из
San Francisco – Сан-Франциска
Culture – культура
separate – отделять, разделять
D.C. (District of Columbia) – округ Колумбия
several - несколько
Dunedin – Данидин
summary – краткое изложение
Glasgow – Глазго
surround - окружать
Government – правительство
Sydney - Сидней
highly developed – высокоразвитый
Tasmania – Тасмания (остров)
industrial – промышленный, индустриальный
territory - территория
include – включать
the English Channel – Английский канал
located – расположенный
Toronto - Торонто
Los Angeles – Лос-Анджелес
tradition – традиция
Exercise № 1. Complete the chart.
| Countries | Geographical characteristics | Population | Capital | Principal towns |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Text B: “The United Kingdom”
The United Kingdom, officially the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, is an island nation and constitutional monarchy in north-western Europe, member of the European Union (EU).
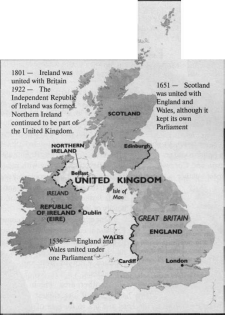
Great Britain is the largest of the British Isles. It comprises, together with numerous smaller islands, England and Scotland, and the principality of Wales. Northern Ireland, also known as Ulster, occupies the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland.
The United Kingdom is bordered to the south by the English Channel, which separates it from continental Europe, to the east by the North Sea, and to the west by the Irish Sea and the Atlantic Ocean. The only land border is between Northern Ireland and the Republic of Ireland. The total area of the United Kingdom is 242 sq.km. The capital and largest city is London.
The names «United Kingdom», «Great Britain», and «England» are often used interchangeably. The use of «Great Britain», often shortened to «Britain», to describe the whole kingdom is common and widely accepted, although strictly it does not include Northern Ireland.
However, the use of «England» to mean the «United Kingdom» is not acceptable to members of the other constituent countries, especially the Scots and the Welsh.
England and Wales were united administratively, politically, and legally by 1543. The crowns of England and Scotland were united in 1603, but the two countries remained separate political entities until the 1707 Act of Union, which formed the Kingdom of Great Britain with a single legislature. From 1801, when Great Britain and Ireland were united, until the formal establishment of the Irish Free State in 1922, the kingdom was officially named the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland.
Hong Kong, which has 200,000 population, was returned to China in 1997.
The mainland of the island of Great Britain is 974 km at its longest and 531 km at its widest; however, the highly indented nature of the island's coastline means that nowhere is more than about 120 km from the sea.
The climate of the United Kingdom is mild relative to its latitude, which is the same as that of Labrador in Canada. The mildness is an effect of the warm Gulf Stream. This current brings the prevailing south-west winds that moderate winter temperatures and bring the depressions which have the main day-to-day influence on the weather. The western side of the United Kingdom tends to be warmer than the eastern; the south is warmer than the north. The mean annual temperature is 6°C in the far north of С in the south-west of England. Winter temperatures seldom areScotland; 11 below -10°C and summer temperatures rarely higher than 32°C. The sea winds also bring plenty of moisture; average annual precipitation is more than 1,000 mm.
Rain tends to fall throughout the year, frequently turning to snow in the winter, especially in Scotland, the mountains of Wales, and northern England. The western side of Britain is much wetter than the eastern: average rainfall varies is from 5,000 mm in the western Highlands of Scotland, to less than 500 mm in parts of East Anglia in England.
The population of United Kingdom is more than 56 mln people, but it is one of the world's leading commercial and industrialized nations. In terms of gross national product (GNP) it ranks fifth in the world, with Italy, after the United States, Japan, Germany, and France.
Vocabulary:
island nation — островное государство
constitutional monarchy — конституционная монархия
European Union — Европейский союз
to comprise — включать
numerous — многочисленные
principality — княжество
North Sea — Северное море
interchangeably — взаимозаменяемо
to accept — принимать, допускать
strictly — строго, зд. строго говоря
include — включать
constituent — составляющий
administratively — административно
entities — зд. субъекты
single — зд. единая
indented — зд. изрезанная
latitude — широта геогр.
prevailing — преобладающий
moderate — умеренный
depressions — зд. циклоны
mean — средний
throughout — на всем протяжении
average annual precipitation — среднегодовое количество осадков
in terms of — говоря (о чем-либо)
GNP (Gross National Product) — валовой национальный продукт.
Exercise № 2 . Translate into English.
1. Официальное название Великобритании — Соединенное Королевство Великобритании и Северной Ирландии.
2. Соединенное королевство является членом Европейского союза и конституционной монархией.
3. Северная Ирландия занимает северо-восточную часть острова Ирландия.
4. Пролив Ла-Манш отделяет Соединенное Королевство от континентальной Европы.
Exercise № 3. Use the following phrases and word combinations to retell the text:
1. As I understood from the text...
2. According to the text...
3. According to the author...
4. As it is described in the text...
5. As it is said in the text...
6. As the author puts it...
7. According to the figures (data, information, opinions) from the text...
Exercise № 4. Discuss the following statements. Use the following phrases to express your opinion:
1. It seems to me (that)...
2. I would like to say that...
3. As I see it...
4. I think that...
5. I guess...
6. I suppose...
7. I (strongly) believe that...
8. I am (absolutely) sure that...
Statement A: The United Kingdom is a small country. It is one of the leading countries now because it had many rich colonies in the past.
Statement B: UK will lose Northern Ireland soon and Wales and Scotland later, like it lost Hong Kong in 1997, because of the differences in languages, culture and history.
Statement C: British people don't travel much because they live not too far from the sea (ocean).
Text C: “History of London”

The Romans were the first to settle and occupy the Celtic fortress of Londinium. Construction of a bridge in 100 A.D. made London an important junction: it soon became a busy commercial and administrative settlement, and in the 2nd century A.D. a wall was built round the city.
The Roman Empire fell in the 5th century. London have maintained its trading activity. In the 9th century Danish invaders destroyed much of the city. They were followed by the Saxons led by King Alfred the Great, who entered the city in 886. The Danes remained a powerful force in England, however, and it was not until the reign of Edward the Confessor, which began in 1042, that civic stability was re-established, to be cemented by the Norman Conquest in 1066.
William the Conqueror centered his power at the Tower of London, and his White Tower is still the heart of this impressive monument.
The City soon united its economic power with political independence. Late in the 12th century it elected its own Lord Mayor. From 1351 it elected its own council, and by the end of the 14th century the reigning sovereign could not enter the City without permission.
In the reign of Elizabeth I had the arts a renaissance with such great dramatists as Shakespeare, Marlowe, and Ben Jonson.
In 1665, London had been devastated first by the Great Plague, and then by the Fire of London, which destroyed most of the city the following year. During the reconstruction of the city, following the original street pattern, the architect Sir Christopher Wren was given responsibility for the design of a number of State-funded buildings, including St. Paul's Cathedral.
The western part of London was developed under the Hanoverian Kings: great squares were laid out such as those of Grosvenor, Cavendish, Berkeley, and Hanover, and more bridges were built across the river. Public services were improved, such as the water supply and sewerage systems, and the streets were paved.
In the 19th century London's population began to rise still more rapidly: it increased sixfold over the century as a whole, thanks to influx from all over the British Isles, from Britain's colonies, and from continental Europe. The Industrial Revolution was creating huge numbers of jobs, but never enough to satisfy the hopes of all the poor people who came to the capital. The novels of Charles Dickens tell us about the social problems of that period.
The First World War had little effect on London, but the Depression that followed in the late 1920s and early 1930s hit the whole country, including the capital. There were hunger marches and riots. London was to pay far more dearly during World War II. The intensive bombing of London (The Blitz) in 1940-1941 took the lives of 10,000 people and left 17,000 injured. Countless historic buildings were damaged, including the Houses of Parliament.
After the war London was to re-emerge as a radically different city. The docks had been so severely damaged that reconstruction, a very expensive process, was not reasonable. By the end of the 1950s most of the war damage had been repaired. New skyscrapers were built, outdoing each other in height and spectacular design. The 30-storey Post Office Tower was built in 1965. It is 189 m high. Other significant post-war developments include the 183 m National Westminster Bank Building (1979); and Britain's highest building, the 244 m Canary Wharf Tower on the Docklands site, near to a new City airport.
General understanding:
1) What was the original name of London? Why was it so important for Romans?
2) Who was King Alfred the Great? When did he enter the city?
3) What is still the reminder of William the Conqueror?
4) How was Britain governed in 12th-14th centuries?
5) How did plague influence the history of London?
6) Who was in charge of the reconstruction of the city? Why did it need reconstruction?
7) Why did the population of London grow in the 19th century?
8) How did the First World War affect the history of London? What about the WWII?
9) How did London change after the WWII?
10) What are the names of skyscraper buildings in London?
Text D: “The United States of America”
The United States of America is the 4th largest country in the world after Russia, Canada and China. It occupies the central part of the North American continent.
The United States of America is a federal republic, consisting of 50 states including the states of Alaska and Hawaii. Outlying areas include Puerto Rico, American Samoa, Guam, and the US Virgin Islands.
The northern boundary is partly formed by the Great Lakes and the St Lawrence River; the southern boundary is partly formed by the Rio Grande. United States also has a sea-border with Russia.
The total area of the United States (including the District of Columbia) is about 9,809,000 sq km.
The country is washed by 3 oceans: the Arctic, the Atlantic and the Pacific. The country has many lakes, with the Great Lakes included. There are also many rivers on the US territory. The longest of them are the Mississippi, the Missouri, the Columbia, the Rio Grande and some others. On the US territory there are mountains and lowlands. The highest mountains are the Rocky Mountains, the Cordillera and the Sierra Nevada. The highest peak, Mount McKinley, is located in Alaska.
The climate conditions are rather different. The country is rich in natural and mineral resources: oil, gas, iron ore, coal and various metals.
The USA is a highly developed industrial and agricultural country. The main industrial branches are aircraft, rocket, automobile, electronics, radio-engineering and others.
Americans are made up from nearly all races and nations. The country population is over 250 mln. The national symbol of the USA is its national flag «Stars and Stripes», having 50 white stars and 13 white and red stripes on its field, symbolising the number of the original and present day states.
Officially the country comprises 50 states and one District of Columbia. The states differ in size, population and economic development. Each state has its own capital. The capital of the USA is Washington. It is situated in the District of Columbia on the banks of the Potomac river and is named after the 1st US President - George Washington. There are many large cities in the country: New York, Los Angeles, Chicago, Philadelphia, Detroit, San-Francisco, Cleveland and some others.
The United States of America is a federal state, headed by the President. According to the US Constitution the powers of the Government are divided into 3 branches: legislative, executive and judicial.
The legislative power belongs to the Congress consisting of the Senate and the House of Representatives. The Senate represents the states while the House of Representatives — the population. The executive power belongs to the President and his Administration (Vice-President and Cabinet of Ministers). The judicial power belongs to the Supreme Court and the system of Federal, state and district courts.
There are several political parties in the USA, the largest of them are the Republican (symbolised by a donkey) and the Democratic (symbolised by an elephant).
Vocabulary:
outlying areas — внешние территории
District of Columbia — округ Колумбия
to pass — проходить через
frontier — граница
to include — включать
lowlands — низины
peak — вершина, пик
to be located — располагаться
aircraft — воздушное судно
to be made up from — быть составленным, состоять из
stripe — полоса
to symbolize — символизировать
legislative power — законодательная власть
to represent — представлять
to belong — принадлежать
donkey — осел
Exercise № 5 . Translate into English:
1. США — четвертая по размеру страна после России, Канады и Китая.
2. Внешние границы включают в себя Пуэрто Рико, Американское Самоа и Виргинские острова.
3.48 Штатов граничат на севере с Канадой, а на юге с Мексикой.
4. США имеет морскую границу с Российской Федерацией.
6. США омывается тремя океанами: Северным Ледовитым, Атлантическим и Тихим.
7. США — высокоразвитое промышленное государство со множеством отраслей.
8. Каждый штат имеет свою столицу.
ADDITIONAL MATERIAL. TEST YOUSELF.
Read the texts about English-speaking countries.
Get ready to answer the questions:
What English-speaking countries do you know?
What countries is the UK made of? What are their capitals?
W'hat can you say about the climate and the weather of the country?
What are the main political parties in the UK?
Who is the British Prime Minister now?
What are the most popular holidays in Britain?
How do people celebrate them?
How many states does the USA consist of?
Who were the first people to live in North America?
Who are the Americans?
Why did so many people go across the sea to the New World?
What stereotypes about Americans do you know?
What is the American dream?
What problems do the Americans face today?
What American holidays do you know?
What are the main political parties in the USA?
Who is the US President now?
What other English speaking countries do you know?
Royal Сoat of Arms of the UK.
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland is an island state: it occupies the territory of the British Isles and is composed of some 5,500 islands, large and small. The two main islands are: Great Britain (in which are England, Wales and Scotland) to the east and Ireland (in which are Northern Ireland and the independent Republic of Ireland) to the west. They arc separated by the Irish Sea.
The UK is one of the world's smaller countries. However, there are only nine other countries with more people, and London is the world's seventh biggest city. The UK is separated from the European continent by the English Channel and the Strait of Dover.The highest mountains are in Scotland and Wales: There are many lakes in Great Britain. On the northwest lies the Lake District, containing the beautiful lakes that give it its name.
The largest cities of Great Britain are:London, Birmingham,Glasgow, Liverpool, Manchester, Sheffield, Bristol, Leeds and Edinburgh. The most important ports are: London, Liverpool, Southampton, Belfast, Glasgow and Cardiff.
The climate in the UK is usually described as cool, temperate and humid. The weather is so changeable that the English often say that they have no climate but only weather. The weather is the favourite topic of conversation in the UK.
The population of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland is over 57 million people. The population lives mostly in towns and cities and their suburbs. Four out of every five people live in towns. The UK is inhabited by the English, the Scottish, the Welsh, and the Northern Irish, who constitute the Britishnation. The British are the descendants of different peoples who settled in the British Isles at different times.
There have been many waves of immigration into Britain. Now there are many people of all colours and races in the UK. These are mostly former inhabitants of lhe former British colonies. These people came to the UK in search of better living standards. Nowadays the policy is to encourage these new immigrant communities to continue speaking their own languages as well as English. The children of immigrants are often taught their own languages in school, and there are special newspapers, magazines, and radio and television programmes for these communities.
The latest wave of immigrants from India, Pakistan, Bangladesh and Hong Kong has of course caused problems. I here is certainly racial tension and racial prejudice in Britain today. In spite of laws passed to protect them, there is still discrimination against Asian and black people, many of whom are unemployed or in low-paid jobs. However, the atmosphere is improving and the different races are slowly learning to trust one another.
The UK is a constitutional monarchy. In law, the Head oi State is the Queen.
In practice, the Queen reigns, but does not rule. The country is ruled by the elective government with the Prime Minister at the head. There are three main political parties in Great Britain: the Labour, the Conservative and the Liberal parties.
Test youself. The UK quiz.
What’s the Queen’s name?
Queen Ann I
Queen Elizabeth II
Queen Margaret II
Where does the Changing of the Guard take place?
Buckingham Palace b. Piccadilly Circus с. Victoria and Albert Museum
What is a double-decker?
A bus
A disco
A taxi
What is Harrods?
A bank
A department store
School
Where can you buy stamps?
At the post office
At the stationer's
At the department store
How many pence are there in 1 pound sterling?
10 b. 100 с. 1000
What is the name of the famous stadium in the north of London?
Wembley b. Westminster с. Wimbledon
Which Liverpool band was so popular in the 60s?
The Beatles
The Police
The Rolling Stones
Where is Nessie supposed to live?
Isle of Man
Loch Ness
River Thames
10/ In Britain, cars are driven on the side of the road.
left-hand
right-hand
wrong-hand
Dame Agatha Christie wrote lots of .
detective stories
plays
Poems
Where is Belfast?
In Northern Ireland
In Scotland
In Wales
Manchester United is a popular team.
basketball
football
Handball
Which famous writer was born in Stratford-upon-Avon?
Samuel Beckett
James Joyce
William Shakespeare
Which king had 6 wives?
Henry IV
Henry V
Henry VIII

The USA. New York. The Statue of Liberty.
The United States of America - the richest and one of the biggest countries in the world - has several names. People say "the United States", "the States", "America", or just "the USA" or "the US".
The United States is a federal union of 50 states, each of which has its own government. According to the US Constitution the powers of the government are divided into 3 branches: the executive, headed by the President, the legislative, exercised by the Congress, and the judical. The Congress consists of the Senate and the House of Representative. There are two main political parties in the USA: the Republican and the Democratic.
The population of the USA is about 250 million. There is no "American climate" or "American countryside". Every part of the country is different, from Alaska in the north, covered with snow and ice, to tropical Florida in the south.

Native American Indians picture.
The American Indians were the first people to live in that vast land.
They had a fascinating, ancient culture, and a rich tradition of language and customs.
When Christopher Columbus arrived, in 1492, there were probably about 1,500.000 Indians in North America. But then, the immigrants came. By the early nineteenth century, the population was more than 17 million. Most came from Europe, but there were also many from the Middle East and the Far East, as well as millions of Africans, caught in the terrible slave trade.
Immigration went on growing. By 1914, the population was 92 million. Now there are more than 25 million British Americans (nearly half the population of Britain), about 23 million African Americans, 25 million German Americans and more Irish Americans than the whole population of Ireland.
You can find almost anything in America. There are .mountains and deserts, old churches and moon rockets, homes with three cars and homes with no electric lights at all. There are people who speak Chinese, Italian, Spanish, Arabic, Polish, Swedish, Japanese - in fact, almost every language under the sun. There is no such thing as a typical American, but there are some views of Americans which many think are fair. Ordinary Americans are friendly and not afraid to show their feelings. They are generous, lively and amusing. They are not as snobbish or class-conscious as the English, and the way people speak is not important to them.
However, there is 'money snobbery' in the USA. The American's dream is success in his job, success earned by his own skill and hard work. There is no one an American admires more that the self-made man, no matter what kind of family he comes from.
Many foreigners have the false idea that there is no public transport in the USA. Since the vast majority of Americans own at least one car, buses aren't necessary, it is believed, so the very poor have to walk. This is quite untrue. There is public transport. There is a cheap and regular bus service in every city. Many cities also have a new subway system, equally cheap. But better-off Americans in many parts of the USA never go by bus. In fact, they wouldn't want to be seen in one in case someone thought they couldn't afford a car!
The USA has many serious problems - crime, violence, unlawful immigration across the Mexican border, pollution, unemployment, race relations. But there has been an improvement in race relations that few non-Americans know much about.
Test youself. The USA quiz.
What are the two major parties in the US?
The Republicans and the Democrats.
The Republics and the Socialists.
The Democrats and the Socialists.
The Conservationists and the Democrats.
How many states are there in the US?
49 b. 50 с. 51 d. 48
What do Americans celebrate on July 4th?
Flag Day.
The Revolution.
с The Discovery of America,
Independence Day.
In which year was the independence from England declared?
a. 1776 b. 1876 c. 1676 d. 1778
Which president freed the slaves?
Thomas Jefferson
George Washington с Abraham Lincoln
Henry Ford
Who was the civil rights leader who fought through non-violent action?
Thomas Paine
Martin Luther King, с John Kennedy
Who was the first person to walk on the moon?
John Glenn
Jim Lowell
с Neil Armstrong
What was the name of the ship that brought the Pilgrims to P England in 1620?
Pitta b. Sunflower с Mayflower
Where’s the White House located?
a. New York b.Washington, D.C. с. Houston
What organisation tries to find solutions to world problems.
The United Nations c. IMF
UNICEF d. Green Peace
What does IMF stand for?
International Monetary Foundation
International Monetary Fund
Internal Monetary Foundation
Internal Monetary Fund
Who said: ’We hold these truths to be self evident that all men I created equal’?
a. Bill Clinton b. George Washington с. Richard Nixon d. Thomas Jefferson
CANADA

Coat of Arms of Canada.
Canada is a good example of the way peoples of different ways of life and different languages can live side by side under one government. The population of Canada has risen from 11.5 million in 1941 to 25 million in 1980. Most of the newcomers are from Europe, Asia and the USA, so that today less than 44% of Canada's population is of British origin. Quebec Province is still 90% French. There are some groups of French Canadians in Ontario and Manitoba, but the numbers are quite small.There are many Indians, Pakistanis and Chinese, and also blacks from the USA, among the immigrants who are pouring into Canada now. All Canadian children have to learn both French and English at school.
The Canadian government is more British in style than American, except that it is a federal government. The head of government is the Prime Minister, often called the PM', as in Britain. The Federal Government has a Senate and House of Commons, and each province also has a House of Commons.

The Maple Tree.
The maple tree is the national tree of Canada. In the fall maple leaves turn a brilliant red and orange. Queen Elizabeth II is still Queen of Canada. She is head of the government, as in Britain, but has a Governor-General to represent her.
Test youself. Canada quiz.
Canada is the second country in the world.
larger b. Large c. largest
The capital Canada is Ottawa.
for b. of c. in
Canada is made ten provinces.
for b. of c. in
The flag of Canada a red maple leaf in the centre.
has b. is c. are
The two official languages of Canada French and English.
has b. is с. are
The first Europeans came Canada for the wealth of fur, fish and forests.
in b. at с. To
The national sport Canada is lacrosse.
a. of b. at с. in
Both basketball and hockey _ first played in Canada.
are b. were с. was
AUSTRALIA

Australian Coat of Arms.
Australia and New Zealand. Here arc some common views that the British have of Australians. Some Australians would agree, others might not. They are fiercely independent and they say exactly what they think, even if it sometimes sounds rude. Five out of six Australians live in the suburbs of towns and cities, and they like to own the house they live in. It is still sometimes said that Australia is not a place for women, and some men still like to spend more time with their mates than with their wives. But more and more Australians have wider interests, now that Australia has citizens from so many different' countries.
NEW ZEALAND

New Zealand Coat of Arms.
New Zealanders are tough, too, but less lively and less carefree. They live just as comfortably, and they have one of the best welfare systems in the world. Hospital treatment costs patients nothing at all. The Australians are becoming more and more attracted towards the USA, but not the New Zealanders, who do not have much love for the Americans. Both Australians and New Zealanders have a great pride in their own countries. They no longer have strong ties with the mother country.
Like the USA, Australia is a federation of states, but both federal and stale governments are run on British, not American lines. The New Zealand Parliament has only one House, which it calls the House of Representatives. Otherwise the whole New Zealand parliamentary system is very like that of the UK. The Queen is head of both Australian and New Zealand governments, but is represented in both cases by a Governor-General.
Test youself. Australia quiz.
In what year did federation take place?
1788
1896
1902
1901
1897
Which day of the year is Australia day?
7 June
26 February
26 January
17 May
7 January
Who was the first Prime Minister of Australia?
James Cook
Edmund Barton
Alfred Deakin
Henry Parkes
Billy Hughes
What is the first line of Australia’s national anthem?
Australia let us all rejoin
Waltzing Mathilda
Australians all let us rejoice
Australia let's all of us rejoice
Australians all let us reach us
What is the floral emblem of Australia?
Waratah
Golden wattle
Royal Bluebell
Sturt's Desert Pea
Red and Green Kangaroo Paw
What is the population of Australia?
21 million
17 million
45 million
92 million
71 million
In what city is the Parliament House of the Commonwealth Parliament located?
London
Sydney
Canberra
Perth
Melbourn
Who is the Queen’s representative in Australia?
John Howard
The Prime Minister
Gordon Brown
The Governor-General
Prince Charles
What are the colours on the Australian flag?
Red, black and yellow
Green, blue, black and white
Red, white and blue
Green, white and yellow
Who is the head of the Australian Government?
The Queen
The President
The Governor-General
The Prime Minister
Try to analise the text about English-speaking countries and find the comparative and superlative d
VI. Test youself. Use the articles where necessary. Pay attention to the notes.
... United Kingdom is situated on ... British Isles.
... British Isles consist of two large islands, ... Great Britain and ... Northern Ireland, and about five thousand small islands.
3.. United Kingdom is made up of four countries: .England, ... Wales, ... Scotland and ... Northern Ireland.
Their capitals are ... London, ... Cardiff, ... Edinburgh, and ... Belfast respectively.
... capital of ... UK is London.
British Isles are separated from the European continent by ... North Sea and . English Channel.
The western coast of ... Great Britain is washed by ... Atlantic Ocean and ... Irish Sea.
... surface of ... British Isles varies very much.
... north of ... Scotland is mountainous and is called ... Highlands.
... north and west of ... England are mountainous.
... Ben Nevis in ... Scotland is ... highest mountain (1.343 m).
There are a lot of rivers in ... Great Britain, hut they are not very long.
... Severn is the longest river, while ... Thames is ... deepest one.
The mountains, ... Atlantic Ocean, and the warm waters of Gulf Stream influence on the climate of . British Isles.
... UK is one of ... world's smallest countries.
... UK is a highly developed industrial country.
It is known as one of ... world's largest producers and exporters of machinery, electronics, textile, aircraft, and navigation equipment.
One of ... chief industries of the country is shipbuilding.
... UK is a constitutional monarchy.
... Queen reigns, but does not rule.
Note that: The use of articles with geographical names has certain patterns.
The name of a river is used with the definite article, and the name of a lake is used without any article. The name of one mountain (or one island) is used without any article, and the name of a mountain chain (or a group of islands) is used with the definite article.
No article: America, North America, South America, Latin America, Europe, Asia, Africa, Australia, Antarctica;
Article the: the Atlantic Ocean,the Pacific, the Arctic Ocean, the Indian Ocean;
No article: Lake Baikal / Baikal, Lake Victoria, Lake Superior, Lake Huron, But: the Great Salt Lake, the Great Lakes (5 lakes).
Article the: (Rivers, straits, canals, currents, waterfalls) the Amazon / the Nile / the Mississippi / the Thames / the Amur /the Strait of Gibraltar,/ the Gulf Stream, the Florida Current,the Panama Canal; the English Channel/ the Victoria Falls.
No article: America, Australia, Great Britain, Britain, England, Canada, Ireland, New Zealand.
Article the: the United States (the U.S.), the United Kingdom (the UK), the Russian Federation, the Netherlands, the Philippines.
No article: (Cities, towns) Berlin, London, Madrid, Moscow, New York, Paris, But: The Hague (Гаага).
TEXTS FOR ADDITIONAL READING
Text 1
THE UNITED KINGDOM OF GREAT BRITAIN AND NORTHERN IRELAND
Britain — an anglicized form of Britannia, the Roman name for what is now England, Wales and Scotland. In the 4th century ВС the inhabitants were known as Pretannoi, and under the Roman occupation they were known as Brittanni.
The British Isles.
The name of Great Britain was first officially used in 1604, when James I was proclaimed 'King of Great Britain'. It had been used earlier by some writers, however, to distinguish Britain from Britannia Minor, or Brittany, in France.
The British Isles refers to the geographical group of islands from near the French coast to the far north near Iceland.
Great Britain refers to England, Wales and Scotland. It is the main island.
The United Kingdom is the administrative title and includes Great Britain and Norrhern Ireland.
Text 2.
England
Read the text about England and find out what special features different regions of England have.
Albion is an ancient and poetic name for England or Great Britain, perhaps from the white (Latin albus) cliffs of Dover, but possibly from Celtic alp, which means 'rock'.
England is often subdivided into three parts: the South, the Midlands and the North:
"This is blessed plot, this earth, this realm, this England. " William Shakespeare
The South. The landscape is varied.
The climate is warmer than in the other areas. There are hundreds of miles of sea coast which vary from flat, sandy or stony beaches to high rocky cliffs. The mild and sunny climate makes the south coast popular with holiday-makers. Some coastal resorts are famous, Brighton among them.
Somerset, Devon and Cornwall are rural counties, tucked away with hidden fishing hamlets and Britain's warmest weather in winter. There are high, bare hills, rock and deep wooded valleys Inland, the landscape is gentle and green; it is famous for its fertile farmland, the calm, tranquil and quiet beauty of its countryside. One of the most beautiful counties in the South of England is certainly Kent. It is known as the Garden of England, because it is famous for its picturesque orchards which produce a lot of fruit and vegetables.
"Our England Is a garden that Is full of stately views ... " Rudyard Kipling
Another area which has some of the richest farmland in the country is known as the Fens and lies to the east of Cambridge.
This land was drained and now the Fen Country consists of miles of flat land with almost no trees or hedges.
A Fen is land which is lowlying and wet, often partly covered with water.
In general, the South is wealthier than other areas of Britain. Work of all kinds is provided on the land, trade and industry. British Aerospace has factories building aeroplanes in several parts of the South. Lots of people are involved in service industries including financial, business and government services, computer services and information systems. There are science-based companies and research organizations.
The Midlands. The Midlands Region has much farming land, but this part of the country is better known as an industrial area, one of England's most productive regions.
Birmingham which is often called the Big Heart of England, is the most important city of the Midlands. It is the second largest city in the United Kingdom. Birmingham and the neighbouring industrial city of Coventry are famous for engineering, especially car production.
Derby is another engineering centre. Rolls Royce make aero engines and cars there.
Rolls Royce a well-known firm founded in 1906 by Charles Stewart Rolls and Henry Royce, is the symbol all over the world of high quality automobile engineering.
The Potteries is another industrial area in the Midlands. It lies around the city of Stoke-on-Trent and produces china, crockery and all kinds of ceramics, some of which are famous worldwide, Wedgwood among them.
Wedgwood is a famous make of pottery and china. The most famous Wedgwood design has raised classical style decorations in white on a pale blue background, named after the potter Josiah Wedgwood (1730 - 95).
The West Midlands, another industrialized area where there are many collieries and steelworks, is known as the Black Country because of the black smoke and blackened buildings there.
In contrast, the Midlands region has some beautiful picturesque countryside in the Peak District with its National Park.
The North. The weather is considerably colder. There is almost always snow in winter.
This is a region of great natural beauty although industry of some kind h.is existed here for hundreds of years. There is a great contrast in the North between the beautiful open, hilly countryside and the industrial towns and mining villages.
In puts of the North — in Yorkshire particularly — title wooded valleys and green pastures and excellent farming land. West Yorkshire is very good country for sheep-farming, and it has long been Britain's most important area for the wool industry. Coal is one of the few natural resources found in the North of England. Some famous industrial cities in the North are Manchester, Sheffield, Leeds and Newcastle-on-Tyne.
What are England’s most remarkable places?
Compare different parts of England.
Where, in your opinion, is most of England s population concentrated? Give your reasons.
Whitehall is a street in central London running from Trafalgar Square to the Houses of Parliament and containing many important buildings and government offices: the Foreign and Commonwealth Offices, the Treasury, Admiralty and Ministry of Defence. In the centre of the roadway stands the Cenotaph, the memorial to the fallen of both world wars. The Prime Minister's residence at No. 10 Downing Street is directly connected to Whitehall.
London is always full of life. The streets are crowded with traffic. High 'double-decker' buses rise above the smaller cars and vans.
The City of London today is the financial powerhouse of the country and one of the chief commercial centers of the western world.
The City has its own Lord Mayor, its own j government and its own police force. Here the medieval buildings stand side by side with modern steel and glass high-rise office blocks. The territory of the City of just I over one square mile contains several banks, including the Bank of England, the Stock Exchange and offices of many financial companies.
The parks of London provide a welcome contrast to the great built-up areas. St. James's Park, Green Park, Hyde Park, and Kensington Gardens are linked together. They form 313 hectares of open parkland in the heart of London.
1. Why is London called the least typical part of Britain while being the capital of the country?
What makes the City of London a powerhouse of the country?
Comment on the words "When a man is tired of London, he is tired of life ".
Read this information about some places of interest in England. Find out:
which of them have historic or literary associations;
which are noted for their outstanding beauty;
which are linked with the sea.
Stonehenge: a prehistoric complex on Salisbury Plain,Wiltshire, regarded as one of the most important monuments of its kind in Europe, and very popular with visitors. The great circle of standing stones is believed to have had some religious or astronomical purpose.
Windsor: a town on the Thames, not far from London. Its castle has been a royal residence for nine centuries. Seen from a distance it is beautiful beyond imagination. Windsor Castle has a long and fascinating history.
Some of the interior apartaments are open to the public when the Sovereign is not in residence.
Canterbury: an ancient city in Kent, with a majestic cathedral which dominates it. Canterbury is a religious capital of England. It was built in the 11th-15th centuries, and became a place of pilgrimage in medieval times after the murder of Thomas a Becket, Archbishop of Canterbury.
Brighton: a popular seaside resort, famous for the architecture of the Royal Pavillion built in an oriental style. Brighton is known for its farge conference centre, where many important political and scientific meeting are held.
Portsmouth: a large city on the south coast particularly rich in associations with the Royal Navy. The flagship of Lord Nelson at the Battle of Trafalgar, Victory, still stands in the port and it ranks as one of Britain's greatest tourist attractions.
Portsmouth is the birthplace of Charles Dickens. The house where he spent his childhood is now a museum.
Text 3.
Places to Visit in England.
London
Read the text about London and find out why it draws people from all over the world.
"When a man is tired of London,he is tired of Life; for there is in Condon all that life can afford." Samuel Johnson (1709-1784).
Today, more than 200 years later, Johnson's words still ring true. There are few places that offer such a variety of sights, entertainments, educational and business opportunities, world-famous museums and theatres, and superb shopping.
London draws people from all over the world. Some come on business, some come to study, to work or on holiday. London is naturally a very English city, yet it is the least typical of Britain as it is very cosmopolitan, containing goods, food and entertainment, as well as people, from many countries of the world.
"London: a nation, not a city. "Benjamin Disraeli
London spreads its influence over much of the southern areas of England; it gives work to millions of people who live not only in the inner-city areas but in surrounding districts. Some people even commute over 100 miles (over 150 km) every day to work in London.
There is much in London which fascinates visitors and inspires the affection of Londoners: the splendour of the royal palaces and the I louses of Parliament, the dignity of St. Paul's Cathedral and many monuments, the fine architecture of numerous historic buildings, and the beautiful parks.
London shows examples of buildings that express all the different areas of its history, it manages in a unique way to reflect its past and at the same time to fulfil the functions of a modern city with its commercialism and bustle.
The name Piccadilly stems from a 17th century dressmaker who lived in the area and created a frilled collar called a 'piccadir.
Buckingham Palace is the official London residence of the Sovereign. The daily ceremony of the Changing of the Guards takes place in its courtyard. The palace was built in 1703 by the Duke of Buckingham. Piccadilly Circus has become an important meeting point — for traffic as well as sightseers. At its heart is a bronze fountain topped by a figure of a winged archer, popularly known as Eros, the pagan god of love. The majority of London's places of entertainment arc concentrated around Piccadilly Circus. This area is now famous for its theatres, clubs and shops.
Text 4.
Wales
Read this information about Wales and find out:
how it is divided geographically;
how industries and agriculture are developing.
Croeso i Cymru — Welcome to Wales
Wales – from old English Wealas, plural of wealh, ‘ foreigner’, applied to the Britons by the Anglo-Saxons. The Welsh name for their own lands is Cymru which means ‘friend’.
Wales is the most bordered on the east by England. It is the smallest land of the United Kingdom, but has considerable variety, from the picturesque mountains of the north to the mining and industrial areas of the south. The main areas of settlement are in the southern valleys and coastal areas, where two-thirds of the population live. The chief cities are Cardiff, Swansea and In 1955 Cardiff was declared the capital of Wales. Wales is a principality (a country ruled by a prince, or from which he takes his title). The title of 'Prince of Wales' is traditionally given by the British sovereign to his or her eldest son, who is heir to the throne. The earliest recorded bearer of the title was Edward II in the early 14th century. The present Prince of Wales is Prince Charles (born 1948) , eldest son of Queen Elizabeth II.
Wales is divided geographically into the industrial south, the central plateaux and lakes, and the mountainous north.
The Welsh Dragon
The exact origin of the Welsh Dragon is lost in the mists of time, and there is still much debate as to its source.
One of the earliest mentions of the Dragon dates to about 800 A.D. References to the Dragon frequently occur in Welsh medieval poetry, where the creature was used to symbolize the country.
The Red Dragon was recognized as the Badge of Wales in 1901, at which time it was added to the Arms of the Prince of Wales.
In 1953, it was made the official Royal Badge of Wales, and after that it became the authorized Welsh National flag.
South Wales. The economy of Wales is based on coal, iron, and steel which are traditional industries in this part of the United Kingdom. The valleys to the north of Cardiff are the heart of the Welsh coal and steel industries.
South Wales remains the principal industrial area. Today Wales is developing as an important centre for electronics, and several new high technology businesses in electronics and related industries have been established.
Agriculture occupies about 80 per cent of the land area; the main activities are sheep and cattle rearing in the hill regions and dairy farming in the lowlands.
North Wales is famous for the wild beauty of its mountains, lakes and waterfalls. With its good coastal resorts, famous for their sandy beaches, and three national parks (Snowdonia, the Brecon Beacons and the Pembrokeshire Coast), as well as other areas of picturesque hill, lake and mountain country, Wales attracts tourists, especially for outdoor holidays.
Text 5.
Places to Visit in Wales
Cardiff Castle: a building representing 1900 years of history. First it was a Roman fort. When the Normans arrived centuries later they built their castle on the site of the old Roman fort. The Castle was strengthened and improved over many years. Its colourful and lavish interiors continually surprise and delight visitors who enter a grim, fighting castle to find themselves surrounded by exquisite wood carving and sculpture, and frescoes that tell of the castle's long history.
Snowdonia: The Welsh call Snowdonia the 'Eagles' Nesting Place', and even though eagles no longer fly here the grandeur of the name is still appropriate for a region that is scenically one of the glories of Britain. The Snowdonia National Park is a region of wild mountains, high passes and craggy peaks. The valleys sparkle with woodfringed lakes and cascading waterfalls. At the centre of the range is Snowdon, the highest mountain in Wales (1085m).
Dinorwig: the largest pumped-storage power station in Europe. It is built in the heart of a mountain to produce electricity by pumping water between two lakes. At all stages of the design and construction it was appreciated that the need to protect the exceptionally fine environment of the Snowdonia Park was of paramount importance. The project took ten years and it was let in 1975.
Ffestiniog Railway (established 23d May 1832 by Act of Parliament). This is a famous railway, with little steam trains which run from the coastline into the mountains. It climbs through tranquil pastures and forests, past lakes and waterfalls, round horseshoe bends and even round a complete spiral, sometimes clinging to the mountainside, sometimes tunneling through it.
The views from the windows of the train are magnificent over countryside set in the midst of the Snowdonia National Park.
Caernarfon: an ancient town with a magnificently preserved castle which dominates it. The son of Edward I, who became the first English Prince of Wales, was born there in 1284. In 1969 Prince Charles was invested there as Prince of Wales. Many episodes in the long history of revolt against English rule took place in the castle, and in the Civil War (1642-1646) it was one of Cromwell's strongholds.
What do you think makes Wales a country interesting for visitors?
What interesting facts about the Welsh Dragon have you found out? What other creatures are used to symbolize different countries?
Who is traditionally given the title of 'Prince of Wales'? Do you think this title is important?
Read this information about Scotland. Find out:
| what its territory looks like; | what industries it is known for; | |
| what climate it has; | what places are interesting to see. | |
Text 6.
Scotland
Caledonia is the Roman name for Scotland but now used only in poetry.
"O Caledonia! stern and wild..." Sir Walter Scott
The ocean bounds Scotland on all sides except for its southern, sixty-mile-long border with England. Most of the country is within forty miles of salt water. On the west coast there are a lot of sea lochs and islands. Most of Scotland's 787 islands are off the northwest coast.
The country may be divided into the Highlands and the Lowlands. However, not all of the Lowlands are really 'low'.
The scenery is beautiful here, so wild and grand — ... I wish an artist had been there to sketch the scene; it was so picturesque — the boat, the nets, and the people in their kilts in the water and on the Shore." from Queen Victoria's diary
The highest peak in the Highlands and in all Britain is Ben Nevis (4406 feet = 1343 m) with its head in cloud and snow towering above the little town of Fort William.
No month has an average temperature below freezing. During the winter months there is usually sufficient snow for skiing. The east coast is drier than the west, where even in summer rainstorms and showers are frequent.
Scotland is famous the world over as a land of beautiful scenery — of hills and valleys, of misty lochs and tumbling rivers, unspoilt beaches and charming fishing villages.
Fishing remains an important activity in Scotland. More than half of the total landings of fish in Britain are made at Scottish ports.
Scotland has about one-third of Britain's total agricultural land, but 71 per cent consists of hill grazing for cattle and sheep. But modern Scotland is also a land of steel and ships, coal and iron. Some of the traditional Scottish industries, such as coal, steel and shipbuilding, are declining. Other traditional manufactures, such as high quality tweeds and other textiles, and food and drink products, remain important. Much is being done to modernize Scotland industry. The electronics sector has greatly contributed to the country's development.
Edinburgh has been the capital of Scotland since 1437. It is an impressive city, situated in one of the most beautiful settings in the world, between the hills and the sea. It is a city of classical architecture and spectacular views, a place of many historic and literary associations.
Text 7.
Places to Visit in Scotland
Edinburgh Castle stands high on the massive grey Castle Rock. The oldest part of the building dates back to about 1100. In the Castle are the Honours of Scotland — the Scottish Crown, scepter and sword of state, the oldest royal regalia in Europe. The imposing Great Hall is still used for banquets and has one of the finest hammerbeam ceilings in Britain.
The Palace of Holyrood is the official residence of the Queen when she is in Scotland. It is one of the most interesting places in Edinburgh. Many events of the long history of Scotland are associated with Holyrood.
Loch Ness is probably Scotland's best known lake, because of the Loch Ness Monster which may live in the deep water. A large prehistoric creature is said to be living in the lake, but it is not scientifically proved to exist. A popular nickname for the Loch Ness Monster is Nessie.
The Burns Country is an area where Scotland's national poet wrote many of the world's most tender love songs. The thatched cottage at Allowav where Robert Burns was born (1759) is the starting point of a heritage trail that links together 40 places associated with the poet.
What do you think makes Scotland a country interesting for visitors?
The rugged landscapes of Scotland create a certain charm and beauty. Do you agree? What poets and writers were inspired by Scotland's grandeur?
You have certainly heard about Loch Ness, the lake that has excited people's curiosity for many years. What do you think stirs the imagination and makes scientists investigate the deep waters of the lake? Are their attempts to find a scientific explanation to the loch's mystery successful?
Text 8.
Northern Ireland
a) Read this information about Northern Ireland and find out:
where the population and industries are concentrated;
what developments are extensive in Northern Ireland;
what places are interesting to visit.
Ireland. The name effectively means 'Eire land', with the first word being the country's Irish name. It may itself mean 'western land', from a word related to Gaelic ‘iar', 'west'; although some authorities derive it from Gaelic 'i', 'island', and 'iarunn', 'iron'. The Roman name of Ireland, Hibernia, evolved as a form of Iverna, itself representing old Celtic Iveriu. This gave Erin as the poetic name for the island.
The landscape of Northern Ireland is gentle. It is green because it rains a lot. But the rain showers quickly change to sunshine — and back to rain again. The mountains roll down to the sea. Northern Ireland is a land of lakes, rivers and a varied sea coast. It is a great place for tourism.
Population and industry are concentrated on the eastern seaboard, while the rest of Northern Ireland remains predominantly rural and relies mainly upon agriculture for its livelihood.
The traditional important industries are shipbuilding and linen. Other industrial activities include the manufacture of textile machinery and a wide range of engineering products, tobacco and clothing. There has also been extensive development in oil-well equipment, electronics, telecommunications equipment, and carpets.
Belfast is one of the youngest capitals in the world. It was here that the 'Titanic' was built and sent out on her fatal maiden voyage to New York in 1912.
The 'Titanic', a British passenger liner, at the time the largest vessel afloat, sank when she collided with an iceberg.
Most of its buildings are comparatively modern. There are many cultural and leisure facilities: the Art Gallery, Belfast Cathedral, the richly-decorated City Hall, the Grand Opera House, the city's excellent Leisure Centres and the Ulster Museum are the main attractions. The Botanic Gardens have rare tropical plants which are 100 years old.
VOCABULARY
| Places | lowland | cathedral |
| area | moor | church |
| attractive | mountainous | citadel |
| breathtaking | pasture | contemporary |
| charming | peak | elaborate |
| county | peninsula | exquisite |
| hamlet | plain | fortress |
| industrialized | plateau (pi. plateaux) | grand |
| lovely | ravine | imposing |
| peaceful | rocky | landmark |
| picturesque | snow-capped | lavish |
| populated | valley | magnificent |
| port | varied | majestic |
| region | waterfalls | masterpiece |
| remote | Climate, Weather | medieval |
| resort | average | modern |
| rural | changeable | outstanding |
| settlement | damp | palace |
| site | mild | present-day |
| splendid | moderate | priceless |
| urban | severe | relics |
| wild | shower | richly decorated |
| Landscape | unpredictable | superb |
| bare | Sightseeing | unforgettable |
| cliff | ancient | unique |
| dale | appealing | up-to-date |
| diverse | art gallery |
|
| flat | castle |
|
Use the information in the texts to answer the questions.
HOW MUCH DID YOU LEARN?
What are the essential differences between Scotland, Wales, Northern Ireland and England?
How does the landscape vary in different parts of the UK and within each of the four countries?
Some places in Britain are known as areas of outstanding natural beauty. Where are they situated? What are they called?
What are the most populated parts of Britain and what are the reasons for the greater concentrations of people in these regions?
Britain has much variety to offer. Lots of people who visit the country are drawn by its history. Which places are regarded as the most important and interesting monuments of the country's history?
Say which part of the UK can be described as:
| • a very popular holiday region; • a most/cosmopolitan place; • a most productive industrial area; • excellent farming land; | • an important coal-mining district; • the wealthiest area; • "the Garden" of England; • the eighth wonder of the world. |
Text 10
State and Government of the UK
Read and translate
The constitutional principles, rules and practices of the United Kingdom have never been codified; they derive from statute law, from common law, and from conventions of the constitution, which are not at all, but political practices which have become considered as dispensable to the smooth working of the machinery of government. The monarchy, followed by the legislative, executive and judicial and of government will be discussed in turn.
A. The monarchy is the most ancient secular institution in the United Kingdom, with a continuous history stretching back over a thousand years. The monarchy is hereditary and the present title to the Crown derives from provisions of the Act of Settlement of 1701 which secured the Protestant succession. This succession cannot now be altered, under a provision of the Statute of Westminster, 1931, except by common consensus of the member states of the Commonwealth which owe allegiance to the Crown.
Queen Elizabeth II, who succeeded to the throne in 1952, is, in addition to being an integral part of the legislature, the head of the judiciary, the commander-in-chief of the armed forces of the Crown and the temporal head of the established Church of England.
The monarchy in the United Kingdom has evolved over the centuries from absolute personal authority to the present constitutional form by which the Queen reigns but does not rule. Her Majesty's government governs in the name of the Queen who must act on the advice of her ministers. The Queen summons, prorogues (dismisses at the end of a session) and dissolves Parliament; she usually opens new sessions of Parliament with a speech from the throne in which the major governmental policies are outlined. These acts form part of the Royal Prerogative, defined by Dicey as 'the residue of discretionary or arbitrary authority, which at any given time is left in the hands of the Crown'. Prerogative rights are of legislative, executive and judicial character. The Monarch must give the Royal Assent before a Bill which has passed all its stages in both Houses of Parliament can become a legal enactment (Act of Parliament). The Monarch's consent and approval is required before a Cabinet can be formed or a minister takes up office. As Head of State the Monarch has the power to sign international agreements, to cede or receive territory, and to declare war or make peace. The Monarch confers honours and makes appointments to all important offices of state, including judges, officers in the armed services, diplomats and the leading positions in the Established Church. As the 'fountain of justice', it is only the Monarch who is able to remit a" or part of the penalties imposed upon persons convicted of crimes through the exercise of the prerogative of mercy on the advice of the appropriate minister.
At the present time the Monarch, although exercising residual authority by consent of Parliament and according to the advice of the government of the day is regularly informed and consulted on many aspects of public affairs. The Privy Council is the body on whose advice and through which the Monarch exercises most statutory and many prerogative powers. There are about 330 members of the Privy Council, which, however, only meets as a full body on the death of the Monarch. It conducts much of its business in committees at which the Monarch may not constitutionally be present. All Cabinet ministers are members; other members are appointed by the Monarch on the recommendation of the Prime Minister.
B. Legislature. Parliament is the legislative organ and is constitutionally composed of the Monarch, the House of Lords, and the House of Commons. The Queen in Parliament represents the supreme authority within the United Kingdom.
(1) The Parliament at Westminster legislates for the United Kingdom, for any one of the constituent countries, or for any combination of them. It may legislate on certain 'excepted' and 'reserved' matters for Northern Ireland, subject to the provisions of the Northern Ireland Constitution Act, 1973. It may also legislate for them Channel Islands and the Isle of Man, under certain conditions, although these islands possess their own ancient legislatures. The Parliament Act, 1911 provides that the life of one Parliament may not exceed five years.
Parliament consists of two Houses: the House of Lords and the House of Commons.
The House of Lords is for the most part still a hereditary body. m consists of the Lords Temporal and the Lords Spiritual. The Lords Temporal include hereditary peers and peeresses who have not disclaimed their peerages under the Peerages Act, 1963; life peers and! peeresses created by the Crown under the Life Peerages Act, 1958 in recognition of public service; and the Lords of Appeal in Ordinary. The House of Lords is presided over by the Lord Chancellor who is ex officio chairman of the House. The Lords Spiritual include the Archbishops of Canterbury and York, the Bishops of London, Durham and Winchester, and the 21 most 'senior diocesan bishops of the Church of England.
The House of Commons is an elected and representative body members (at present 650) are elected by almost universal adult suffrage! to represent constituencies in England (523), Scotland (72), Wales (38)1 and Northern Ireland (17). The law relating to Parliamentary elections is contained in substance in the Representation of the People Act, 1949, amended. Any British subject aged 21 or over, not otherwise disqualified (as for example, members of the House of Lords, certain clergy, undischarged bankrupts, civil servants; holders of judicial office, members of the regular armed services and the police forces) nay be elected a Member of Parliament (M.P.). Members are paid a salary and an allowance for secretarial and office expenses; after a parliament is dissolved all seats are subject to a General Election. By-elections take place when a vacancy occurs during the life of a parliament, as when a member dies, is elevated to the House of Lords or accepts an 'office of profit' under the Crown.
The Speaker of the House of Commons is elected by the members from the members to preside over the House immediately after each new Parliament is formed. He is an impartial arbiter over Parliamentary procedure and the traditional guardian of the rights and privileges of the House of Commons.
The supremacy, or sovereignty, of the United Kingdom Parliament is probably the most basic principle of British constitutional law. Parliament has of its own will settled the duration of the life of a Parliament, acts in such a way as not to bind its successors in the manner or form of their legislation, and, in the Parliament Acts of 191 1 and 1949 has provided that in certain circumstances a Bill may become law without the concurrence of all the component parts of Parliament. These two Acts have clarified the supremacy of the House of Commons over the House of Lords, which can only delay the passage of Public Bills for a maximum period of one year and cannot delay at all the passage of Money Bills (financial measures).
The European Communities Act, 1972 (c. 68), which made legislative changes in order to enable the United Kingdom to comply with the obligations entailed by membership of the European Coal and Steel Community, the European Economic Community, and the European Atomic Energy Community, from 1 Jan. 1973, gives the force of law in the United Kingdom to existing and future Community law which under the Community treaties is directly enforceable in member states, and provides for subordinate legislation in connection with the implementation of obligations or the exercise of rights derived from the Community Treaties.
(2) The Parliament of' Northern Ireland established by the Government of Ireland Act, 1920, was abolished and replaced by the Assembly elected under the provisions of the Northern Ireland Assembly Act, 1973 (supra Introduction preceding: I). The first Northern Ireland Executive agreed upon by this Assembly took office in November 1973, but collapsed in May 1974. Direct rule by the Parliament at Westminster has been reimposed, under the provisions of the Northern Ireland Constitution Act, 1973, in consequence.
С. Executive. – The government consists of the ministers appointed by the Crown on the "recommendation of the Prime Minister, who is appointed directly by the Crown and is the leader of the political party which for the time being has a majority of seats in the House of Commons. The office of Prime Minister dates from the eighteenth century and is the subject of a number of constitutional conventions. The Prime Minister is the head of the government and presides over meetings of the Cabinet; by convention he is always a Member of the House of Commons. He consults and advises the Monarch on government business supervises and to some extent coordinates the work of the various ministries and departments and is the principal spokesman for the government in the House of Commons. He also makes recommendations to the Monarch on many important public appointments, including the Lord Chief Justice, Lords of Appeal in Ordinary, and Lords Justices of Appeal.
The Cabinet is the nucleus of government; its members consist of a small group of the most important ministers who are selected by the Prime Minister. The size of the Cabinet is today about 23 and its principal function, much of the work being carried out in Committee, is to determine, control and integrate the policies of the government for submission to Parliament. The Cabinet meets in private and its deliberations are secret; no vote is taken, and, by the principle of 'Cabinet unanimity', collective responsibility is assumed for all decisions taken.
The central government ministries and departments give effect to government policies and have powers and duties conferred on them by legislation, and, sometimes, under the Royal Prerogative. Each is headed by a minister who is in most cases a member of either the House of Lords or the House of Commons. There are over 100 ministers of the Crown at the present time; they include departmental ministers (e.g., the Secretary of State for Foreign and Commonwealth Affairs; Chancellor of the Exchequer (Treasury); Secretary of State for Social Services); non-departmental ministers (e.g., Lord President of the (Privy) Council, Paymaster-General, Ministers without Portfolio); ministers of state (additional ministers in departments whose work is heavy); and junior ministers (usually known as Parliamentary Secretary or Parliamentary Undersecretary) in all ministries and departments.
The Lord Chancellor and the Law Officers of the Crown deserve special mention at this point. The Lord High Chancellor of Great Britain presides over the House of Lords both in its legislative capacity and as a final court of appeal; he is a member of the Cabinet and also has departmental responsibilities in connection with the appointment of certain judges. He advises on, and frequently initiates, law reform programmes with the aid of the Law Commissions, the Law Reform Committee and ad hoc committees. The four Law Officers of the Crown include, for England and Wales, the Attorney-General and the Solicitor-General; for Scotland, the Lord Advocate and the Solicitor General for Scotland. The English Law Officers are usually members of the House of Commons and the Scottish Law Officers may be. They represent the Crown in civil litigation, prosecute in certain exceptionally important criminal cases, and advise government on points of law. They may appear in proceedings before the International Court of Justice, the European Commission of Human Rights and Court of Human Rights. They may also intervene generally in litigation in the United Kingdom as representatives of the public interest.
The United Kingdom has no Ministry of Justice. Responsibility for the administration of the judicial system in England and Wales is divided between the courts themselves, the Lord Chancellor, and the Home Secretary. The Lord Chancellor is concerned with the composition of the courts, with civil law, parts of criminal procedure and law reform in general; the Home Secretary is concerned with the prevention of .criminal offences, the apprehension, trial and treatment of offenders, and with the prison service.
Exercises and tasks
1. Прочитайте заголовок текста и расскажите в общих чертах, о чем может идти речь в этом тексте.
2. Вспомните, что Вам известно о государственных органах и правительстве Великобритании и запишите основные факты в свою тетрадь.
3 Посмотрите текст и выпишите из него все слова и выражения, которые Вам знакомы.
4 Выпишите все английские слова, относящиеся только к данной
теме и расположите их в алфавитном порядке. Напишите к ним
русские эквиваленты.
5. Разбейте текст на абзацы. Озаглавьте каждый абзац по-английски.
6. Посредством одного предложения передайте главное содержание каждого абзаца.
7. Мы полагаем, что текст можно разделить на три основные
части/темы topics:
The monarchy
The legislature
The executive
Вы согласны с этим?
8. Discuss these topics in pairs or in small groups under the leadership
of your English teacher.
9. False or true? Check your answers in the text.
The monarchy is the most ancient secular institution in the UK.
The constitutional principles, rules and practices of the United Kingdom have never been codified.
The Queen summons, prorogues and dissolves Parliament. She usually opens session of Parliament with a speech from the throne.
As Head of State the Monarch has the power to sign international
agreements and to declare war or make peace.The Monarch must not give the Royal Assent before a Bill which has passed all its stages in both Houses of Parliament can become a legal enactment (Act of Parliament). All Cabinet ministers are appointed by the Monarch on the recommendation of the Prime Minister.
6. Parliament consists of three Houses.
7. The House of Commons is not an elected and representative body.
8. The Prime Minister confers honours and makes appointments to all important offices of state, including judges, officers in the armed services, diplomats.
10. What is meant by State Organs?
11. Explain the difference in meaning between the two verbs in the
following phrase "The Queen reigns but does not rule". What do
you understand by this?
12. Use the context to decide what a Bill is.
13. What do you understand by the prerogative of mercy? Use the context to help you.
14. Read section a of the text carefully and name all the functions
power, duties, obligations of the Monarch?
15. What state body is the Privy Council?
16. When did Queen Elizabeth II become queen?
17. What role does the monarch have in the UK at present?
18. Who summons, prorogues and dissolves Parliament in Russia?
When?
19. Read section b of the text carefully and write down the most important information about this state organ.
20. Read section с of the text carefully. Use the dictionary to help you. Then explain the term "Executive" in English to other students.
21. Ask one of the students to tell you about Executive in detail.
22. Translate the last paragraph "The United Kingdom has Ministry of
Justice..."
23. Read the whole text again and discuss the subject "The UK System of Government" in your group.
24. Compare the State and Government in the UK with the State and
Government in Russia and find out the differences and similarities
between them.
25. Name the state organs of the UK and Russia.
26. Are these phrases synonymous?
The monarchy is most ancient secular institution in the UK?
The monarchy is most ancient non-religious institution in UK.
27. Find in the text all the synonyms for "состоять из".
28. Put the following sentences in the correct order.
The Queen, act, must, the advice, on, misters, her, of, Parliament, of, to consist, Houses, two.
29. Complete the sentence. Use the text to help you. "The Parliament of Northern Ireland..."
30. Complete the following sentences with the missing parts below:
Parliament is dissolved by the Queen...
The Queen must act...
VOCABULARY
| indispensable, adj | необходимый, обязательный, непреложный |
|
| machinery of government | органы управления |
|
| constitutional practice | конституционная практика/конституционный обычай |
|
| to derive from | происходить от, устанавливать происхождение, производить (слово) |
|
| judicial, adj | судебный, судейский |
|
| judiciary, n | суд, судебная власть, судебная система |
|
| legislative, adj | законодательный |
|
| executive, adj | исполнительный, административный; исполнительная власть, правительство |
|
| secular, adj | светский |
|
| monarchy, n | монархия |
|
| hereditary, adj | наследственный |
|
| title, n | титул, звание |
|
| the Act of Settlement | закон о престолонаследии (в Англии) |
|
| succession, n | правопреемство; наследование |
|
| Westminster, я | Вестминстер (район Лондона); английский парламент |
|
| Commonwealth, n | Содружество |
|
| allegiance, n (to) | верность, лояльность, преданность |
|
| to owe | быть должным кому-л.; быть обязанным кому-л .быть в долгу перед кем-л. |
|
| to succeed to the throne | наследовать трон/ престол |
|
| the Commander-in-Chief of the armed forces | главнокомандующий вооруженными cилами |
|
| to reign | царствовать, царить, господствовать, править |
|
| to summon | созывать |
|
| to govern | управлять, руководить, регулировать |
|
| to prorogue | отсрочить, назначать перерыв в работе парламента |
|
| to dismiss | отклонять иск; увольнять, освобождать от должности |
|
| to outline | наметить в общих чертах |
|
| in outline | в общих чертах |
|
| royal prerogative | королевская прерогатива |
|
| Royal assent | королевская санкция (принятого парламентом закона) |
|
| Act of Parliament | акт парламента, парламентский закон |
|
| to have the power | иметь право, полномочие, правомочие |
|
| to sign international agreements | подписывать международные соглашения |
|
| to cede | передавать, уступать |
|
| to declare war | объявлять войну |
|
| to make peace | устанавливать мир |
|
| to make appointments to all important offices | назначить на все вакантные посты/должности |
|
| to remit | прощать, помиловать, освобождать (от штрафа, наказания, ответственности) |
|
| the House of Lords | палата лордов |
|
| the House of Commons | палата общин |
|
| the Speaker of the House of Commons | спикер палаты общин |
|
| Head of State | глава государства |
|
| supremacy | Верховенство, примат, супрематия |
|
| sovereignty | суверенитет |
|
| sovereign | суверен, монарх |
|
| King’s speech | тронная речь |
|
| Queen’s/royal/sovereign’s speech | тронная речь |
|
| the Lord Chancellor | лорд-канцлер (член кабинета министров в Великобритании, спикер штаты лордов, председатель Верховного Суда) |
|
| the Home Secretary | министр внутренних дел |
|
| the Ministry of Justice | министерство юстиции |
|
| Privy Council | член тайного совета |
|
(Theodore H. White)
Text 11
A New Nation
Read and answer the questions.
In 1776, the thirteen weak British colonies in America came together, stood up, and told what was then the world's greatest power that from now on they would be free and independent states. The British were neither impressed nor amused, and a bitter six-year war followed, the Revolutionary War (1776-83). It's hard to appreciate today, over two centuries later, what a revolutionary act this was. A new republic was founded, turning into reality the dreams and ideals of a few political philosophers. Americans broke with an age-old tradition, and so sent shock waves back across the ocean: they decided that it was their right to choose their own form of government. At that time, the statement that governments should receive their powers only "from the consent of the governed" was radical indeed. Something new was under the sun: a system of government, in Lincoln's words, "of the people, by the people, for the people".
Do you know? Work in groups, and try to give answers to the following questions about the beginning of the US history.
When was America discovered?
Who were the original inhabitants of the American
continent?When did the first settlers from England arrive in
America? What was the name of their ship?Who were these people? Why do you think they left their homes for
an unknown land?What was the first state of the US?
What is the oldest big city in the US?
What was the first name of New York?
What is the name of the region where the oldest American states are situated?
Have you ever heard of the "Boston tea party"? What is it?
Why is America often called a "melting pot"?
Text 12.
The US System of Government
The United States of America (USA), consisting of 50 States and the District of Columbia, is a presidential Republic. The total area of the USA is over nine million square kilometres. The population of the USA is about 250 million people. The capital of the USA is Washington. American English is the official language of the USA.
The legislative branch of the US Government, or the Congress, represents all of the American states. It consists of two parts: the House of Representatives and the Senate. Each state has two senators, who are elected every 6 years. A senator must be at least 30 years old, a citizen of the United States for 9 years, and live in the state she or he will represent. A representative must be at least 25 years old, a citizen for 7 years, and live in the state.
The job of the Congress is to make laws. The President can veto a bill. The Congress can pass the law anyway if it gets a two-thirds majority vote. The Congress can also declare war. The House of Representatives can also impeach the President. This means that the House can charge the President with a crime. In this case, the Senate will put the President on trial. The Senate votes to approve the justices that the President appoints to the Supreme Court.
The executive branch of the government puts the country's laws into effect. The President of the United States is a member of the executive branch. The President must be at least 35 years old, and be a natural citizen of the USA. In addition, he must have lived in the US for at least 14 years, and be a civilian. The President is elected every four years and cannot serve more than two terms. The Vice-President of the USA is - president of the Senate. When the President receives a bill from the Congress, he must sign it, and then the bill becomes a law. However, if he disagrees with the law, he can veto it. The President can also ask the Congress to declare war. He also appoints the justices to the Supreme Court. He must do his job according to the Constitution, or he may be impeached.
The judicial branch of the government is the system of courts jn the United States. Its job is to enforce laws. The Supreme Court is the highest court in the country. It consists of 9 justices: one Chief Justice and 8 associate justices. The President appoints the justices, but the Senate must approve them. The justices are appointed for life. The Supreme Court makes sure that people obey the laws. The Supreme Court can also decide if a law is constitutional, that is, if it is in agreement with the Constitution. The judicial branch works together with the legislative and executive branches to protect the Constitution and the - rights of people.
Three different lawmaking groups exist in the United States: (1) legislatures, (2) agencies, and (3) courts. Legislatures pass laws directly, agencies develop laws that help put legislative rulings into effect, and courts establish laws as a result of case decisions.
The White House is the President's residence.
The US national flag - Stars and Stripes - is red, white and blue. 13 strips represent the original 13 states of the USA; the 50 stars represent the current number of states of the USA.
Learn the following words and phrases!
VOCABULARY
| the total area | общая площадь |
| to insure domestic tranquility | обеспечивать общественный порядок / правопорядок на территории страны |
| to promote the general welfare | содействовать укреплению всеобщего благосостояния |
| to establish a constitution | обнародовать конституцию |
| Congressman, n | член палаты представителей конгресса США/конгрессмен |
| lawmaking, n | правотворчество / законотворчество / издание законов |
| lawmaker, n | законодатель / субъект правотворчества/член законодательного собрания |
| All legislative powers are in- vested in a Congress of the United States. | Конгресс США олицетворяет собой всю зак нодательную власть / Вся законодательна! власть принадлежит / предоставлена конгрессу |
| a presidential republic | президентская республика |
| the legislative branch of the government | законодательная власть |
| the Congress | конгресс (законодательная власть в США) |
| to represent smb., smth. | представлять кого-либо, что-либо |
| the House of Representatives | палата представителей |
| the Senate | сенат (верхняя палата конгресса США) |
| a senator / member of senate | сенатор штата / член сената США |
| to be elected as President | быть избранным президентом |
| to be a citizen of the United States | быть гражданином США |
| a representative | представитель |
| to make a law | создавать закон / издавать закон |
| to veto a bill | наложить вето на законопроект |
| to pass the law to get a two-thirds majority vote | принимать закон получить большинство в две трети голосов |
| to declare war | объявить войну |
| to impeach the President | подвергнуть президента импичменту |
| to charge the President with a crime | обвинить президента в совершении преступления |
| to put the President on trial | судить президента / предать президента суду |
| to vote | голосовать |
| to pass a bill | принимать / утверждать законопроект |
| to approve the justices | утвердить судей |
| to appoint a justice to the Supreme Court | назначить судью Верховного суда |
| the executive branch of the government | исполнительная власть |
| to put the country's laws into effect | приводить в исполнение законы страны |
| to be natural citizen of the USA | родиться в США и быть гражданином США |
| to serve | служить |
| a term | срок / срок полномочий / наказания |
| the Vice-President | вице-президент |
| to sign an agreement | подписать соглашение |
| the judicial branch of the government | судебная власть |
| a system of courts | система судов |
| to enforce law | применить закон |
| a justice | судья |
| Chief Justice | верховный судья |
| an associate justice | член суда |
| to be appointed for life | назначаться пожизненно |
| to obey the law | подчиниться закону |
| constitutional | конституционный |
| the protect of the Constitution and rights of people | защищать конституцию и права граждан |
| The Congress of the United States consists of a Senate and House of Representatives | Конгресс США состоит из сената и палаты представителей. |
| The House of Representatives is composed of members chosen every second year by the people of the several states. | Палата представителей состоит / формируется из представителей от каждого штата, избираемых гражданами сроком на два года. |
| The House of Representatives has to choose their Speaker and other officers; and the sole power of impeachment. | Палата представителей избирает своего спикера и других должностных лиц / чиновников и имеет исключительное право импичмента (процедура привлечения к ответственности высших гражданских должностных лиц). |
| The Senate of the United States is composed of two senators from each state chosen for six years; and each senator has one vote. | Сенат США включает два сенатора от каждого штата, избираемых на 6 лет, и каждый сенатор имеет один голос. |
| the protection of the rights of the citizens | защита прав граждан |
| A constitutional amendment can only be carried if a very substantial majority, both in Congress and the individual states, approve it. | Поправка может быть внесена в конституцию лишь в том случае, когда она получает одобрение значительного большинства как в конгрессе, так и в каждом штате. |
| Who can alter the rules of the U.S. Constitution? | Кто может изменить положения / статьи конституции США? |
| Does the USA have a written constitution? | США имеют писаную конституцию? |
| When was the American constitution first written? | Когда была впервые написана конституция США? |
| The Constitution of the United States was reduced to writing in 1787. | Конституция США была написана в 1787 г. |
| Can it be changed? | Она может быть изменена? |
| The Democratic Party is one of the two major political parties in the U.S., founded in 1828. | Демократическая партия - одна из двух главных политических партий США, основана в 1828г. |
| The Republican Party is one of the two major political parties in the U.S., originated 1854-1856. | Республиканская Партия - одна из двух главных политических партий США, основана в 1854-1856 гг. |
| fundamental law (constitution) | основной закон (конституция) |
| legal state | правовое государство |
| threat to a legal state | угроза правовому государству |
| observe the principles of a legilstate | соблюдать принципы правового государства |
| US Administration | Администрация США (правительство) |
| federal government | органы федеральной власти |
| state government | органы власти штатов |
| local authorities | местные органы власти |
| The US is a presidential republic. | США - президентская республика. |
| There are 50 states in the US. | В США - 50 штатов. |
| The capital of the US is Wash ington, D.C. (District of Columbia). | Столицей США является Вашингтон, округ Колумбия. |
| The executive power belongs to the President. | Исполнительная власть принадлежит Президенту. |
| The President is elected together with a Vice-President for a term of 4 years. | Президент избирается сроком на 4 года вместе с вице-президентом. |
| The Presidential election is held every 4 years in November on Tuesday after the first Mon- day. | Президентские выборы проходят раз в четыре года в ноябре во вторник после первого понедельника. |
| The White House is the Presi- dent's residence. | Резиденция Президента-Белый дом. |
| The highest legislative body is the Congress. | Высшим законодательным органом США является Конгресс. |
| Congressmen | члены Конгресса |
| Capitol | Капитолий (здание Конгресса) |
| The Congress consists of two chambers. | Конгресс состоит из двух палат. |
| Senate | Сенат |
| House of Representatives | Палата представителей |
| In order to become a law all bills must pass the Houses and must be signed by the President. | Чтобы стать законом, все законопроекты должны пройти через обе палаты и быть под- писаны Президентом. |
| The US Supreme Court is the highest judicial body. | Верховный суд США является высшим судебным органом. |
| State Department | Государственный департамент |
| State Secretary | Государственный секретарь |
| Chief Justice | Председатель Верхового суда |
| governor of state | губернатор штата |
| appoint heads of departments | назначить глав министерств |
| Democratic Party | Демократическая партия |
Похожие файлы
object(ArrayObject)#864 (1) {
["storage":"ArrayObject":private] => array(6) {
["title"] => string(150) "Использование мультимедийного учебного пособия на занятиях по английскому языку"
["seo_title"] => string(80) "ispolzovanie_multimediinogo_uchebnogo_posobiia_na_zaniatiiakh_po_angliiskomu_iaz"
["file_id"] => string(6) "564213"
["category_seo"] => string(15) "angliiskiyYazik"
["subcategory_seo"] => string(7) "prochee"
["date"] => string(10) "1606136537"
}
}
Подтверждение авторства
Пожалуйста, введите ваш Email.
Если вы хотите увидеть все свои работы, то вам необходимо войти или зарегистрироваться
Полезное для учителя
* Свидетельство о публикации выдается БЕСПЛАТНО, СРАЗУ же после добавления Вами Вашей работы на сайт




















